Elements
Last updated: March 17, 2025
Web Fragments uses custom elements as an implementation detail to embed applications in an existing user-interface. By using custom elements keep the implementation lightweight and benefit from using shadowRoot for style encapsulation.
Additionally, all scripts of the fragment application execute in an isolated JavaScript context.
Custom elements registration
Before using the Web Fragments on the client-side of an application, the library needs to be initialized via exported initializeWebFragments() function:
import { initializeWebFragments } from "web-fragments";
initializeWebFragments();
This initialization should occur as early as possible during the bootstrap of a the existing application.
Please notice that different frameworks may require additional utilities to work with custom elements. For example Angular needs CUSTOM_ELEMENTS_SCHEMA to be provided.
The <web-fragment> element
<web-fragment> is a custom element responsible for marking the location in the existing application where a Web Fragment should be nested.
<web-fragment> have a fragment-id attribute to uniquely identify the fragment.
<web-fragment fragment-id="some-id"></web-fragment>
By default, <web-fragment> will create a bound fragment, which shares (binds) window.location and navigation history with the existing application that contains the fragment. The window.location in a bound fragment is initialized to the current window.location of the top level application. Navigation initialized from the existing application or a web fragment will be reflected in both contexts.
Optionally, a fragment can be created with the src attribute, which specifies the url from which the fragment should be initialized. This will cause a creation of an “unbound” fragments, which has its own window.location and history, both of which are independent of that of the rest of the application or other fragments.
Both bound and unbound fragments run in a dedicated JavaScript context through reframing — a virtualization technique unique to Web Fragments.
Server-side piercing
Server-side piercing refers to he process through which the legacy app shell is combined with the server-side rendered HTML stream of a fragment.
It allows the eager display and initialization of a fragment at the moment of bootstrapping the shell application.
piercing-styles configured during fragment registration, help positioning the fragment in the correct slot.
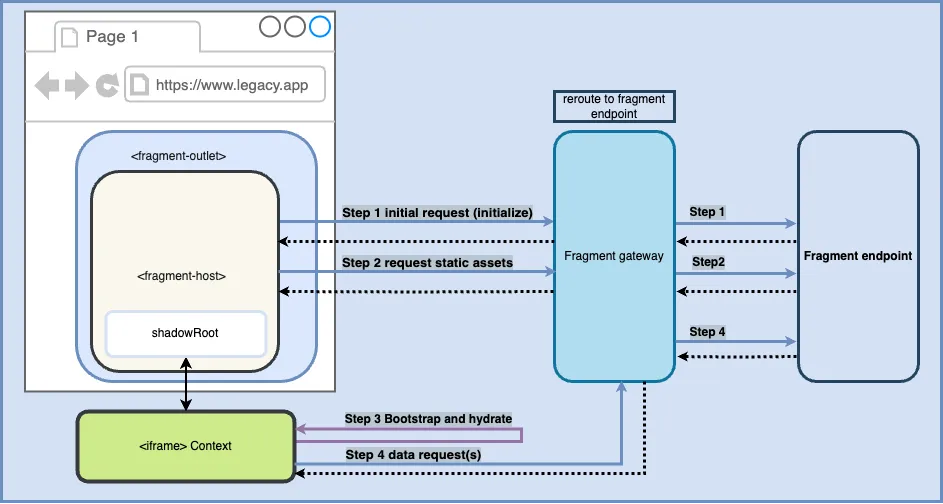
Routing of fragment’s requests
All requests initiated from DOM or JavaScript of a fragment are intercepted by the fragment gateway middleware. This middleware sits in front of the legacy application, identifies requests originating from the fragment via the routePattern in the fragment registration configuration, and reroutes all assets requests to the right fragment endpoint.
Learn more about middleware in the gateway section.